Solar energy is rapidly becoming a popular choice for homeowners and businesses worldwide, aiming to reduce their carbon footprint and save on energy costs. When it comes to solar systems, two main types stand out: off-grid and on-grid. Each has its unique features and benefits, and choosing the right one depends on your specific needs and circumstances.
On-Grid Solar Systems: A Reliable and Efficient Choice
On-grid solar systems, also known as grid-tied systems, are designed to connect directly to the electric grid. These systems provide a reliable source of electricity, supplementing the power you receive from your utility company. A significant advantage of on-grid systems is their ability to feed unused energy back to the grid through net metering. This means that when your solar panels generate more electricity than you consume, the excess energy is credited to your account, reducing your electricity bills.
Inverters play a crucial role in on-grid solar systems. They convert the direct current (DC) electricity generated by your solar panels into alternating current (AC), which is used in your home or business. The inverters also enable the reverse power flow, sending excess energy back to the grid. This feature ensures that you never waste the solar energy you generate, and it can significantly reduce your energy bills.
Another significant benefit of on-grid solar systems is the grid power backup. If your solar panels are not producing enough energy or your batteries are depleted, you can still rely on the grid for electricity. This can provide peace of mind, especially for homeowners who may be concerned about whether they can generate sufficient solar power to go completely off-grid.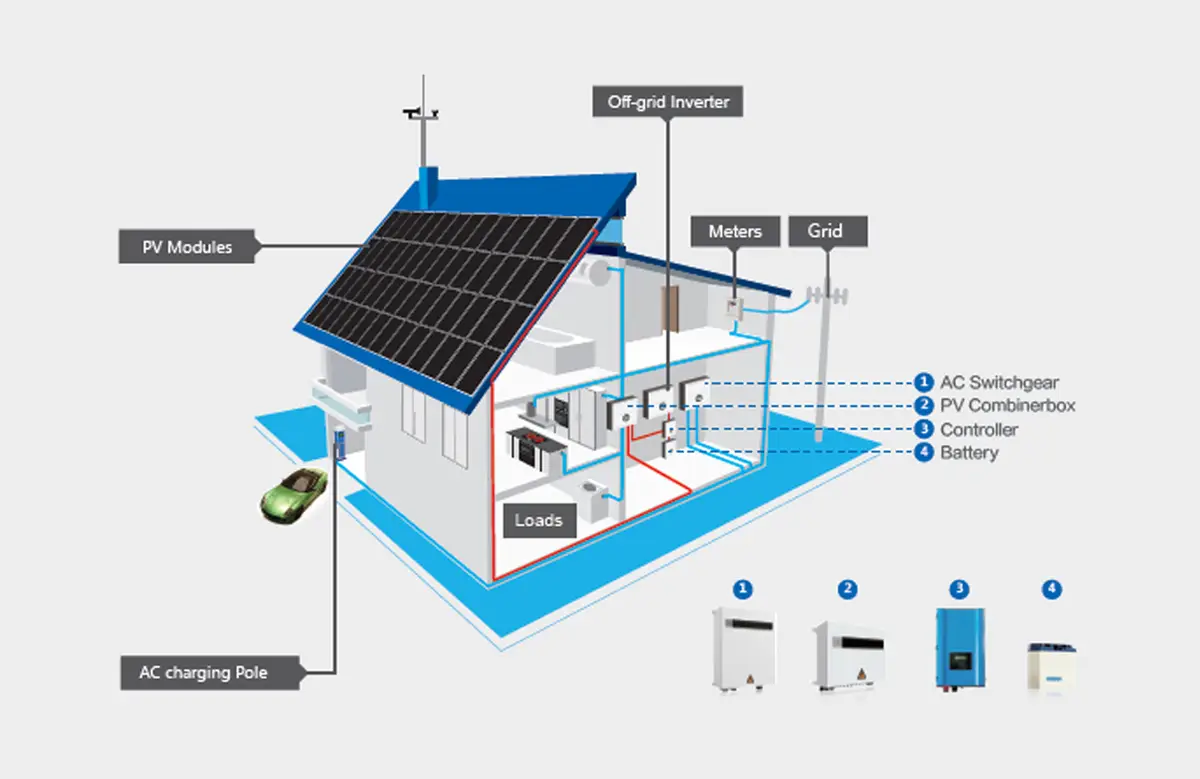
Off-Grid Solar Systems: Independence and Resilience
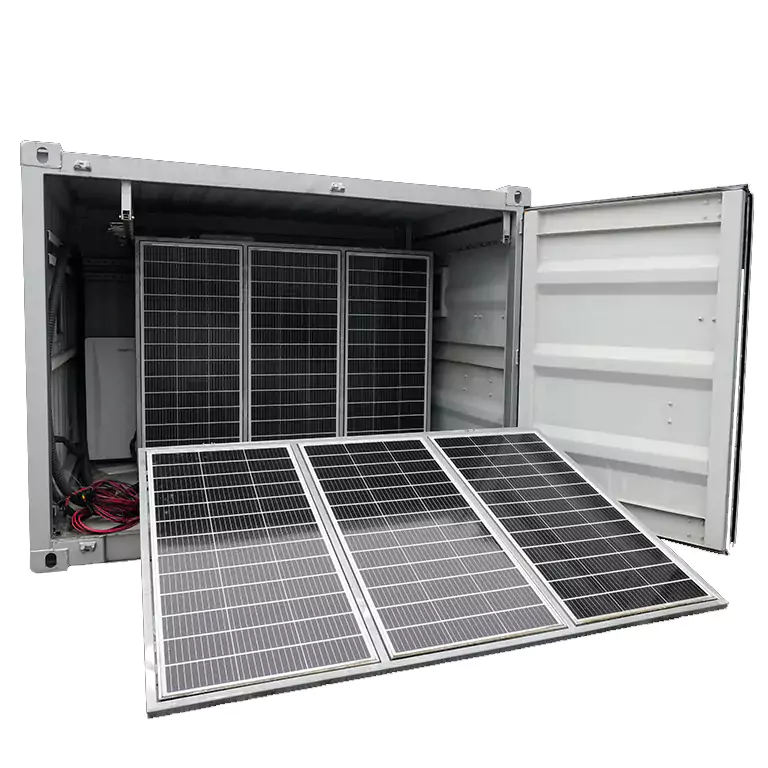
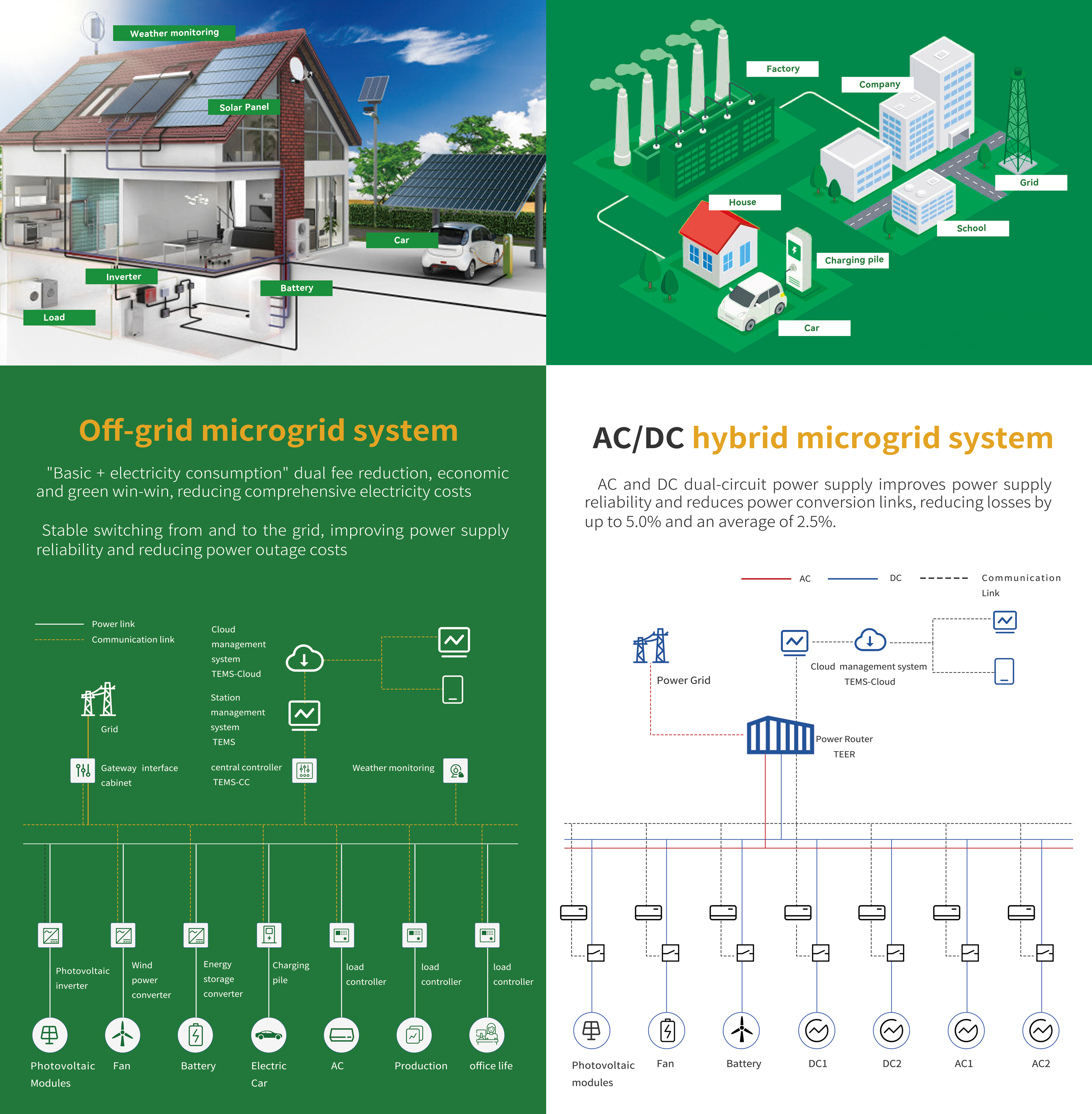
Off-grid solar systems, on the other hand, are entirely self-sufficient and not connected to the electric grid. They rely on battery storage to store the electricity generated by solar panels. As a result, off-grid systems are ideal for remote locations where connecting to the grid is not practical or feasible. They are also popular among homeowners who want to be completely independent of the grid.
One of the key advantages of off-grid solar systems is their resilience against power outages. Since they are not connected to the grid, they are not affected by power failures or disruptions. As long as you generate and store sufficient solar power, you will have electricity even when the grid goes down. This feature can be particularly important in areas prone to natural disasters or other emergencies.
Off-grid solar systems also offer flexibility and scalability. You can expand your battery and output capacity as your power needs grow, ensuring that you always have enough electricity to meet your demands. For example, the EcoFlow DELTA Pro Solar Generator allows you to expand your system as needed, ensuring that you always have a reliable source of energy.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solar System for Your Needs
Both on-grid and off-grid solar systems offer significant benefits, and the right choice depends on your specific needs and circumstances. On-grid systems provide a reliable source of electricity, reduce your energy bills, and offer grid power backup. Off-grid systems, on the other hand, offer independence and resilience against power outages, with the flexibility to expand as your power needs grow.
Ultimately, the best solar system for you will depend on your location, energy needs, and budget. By understanding the differences between on-grid and off-grid solar systems, you can make an informed decision that meets your specific requirements and helps you reduce your carbon footprint while saving on energy costs.

















 Inquiry
Inquiry Online Chat
Online Chat