In the quest for sustainable and cost-effective energy solutions, home solar systems have emerged as a popular choice for households worldwide. Not only do they help reduce our reliance on fossil fuels, but they also provide a reliable and eco-friendly source of electricity. This comprehensive guide delves into the anatomy of home solar systems, their installation process, application types, and a balanced assessment of their advantages and drawbacks.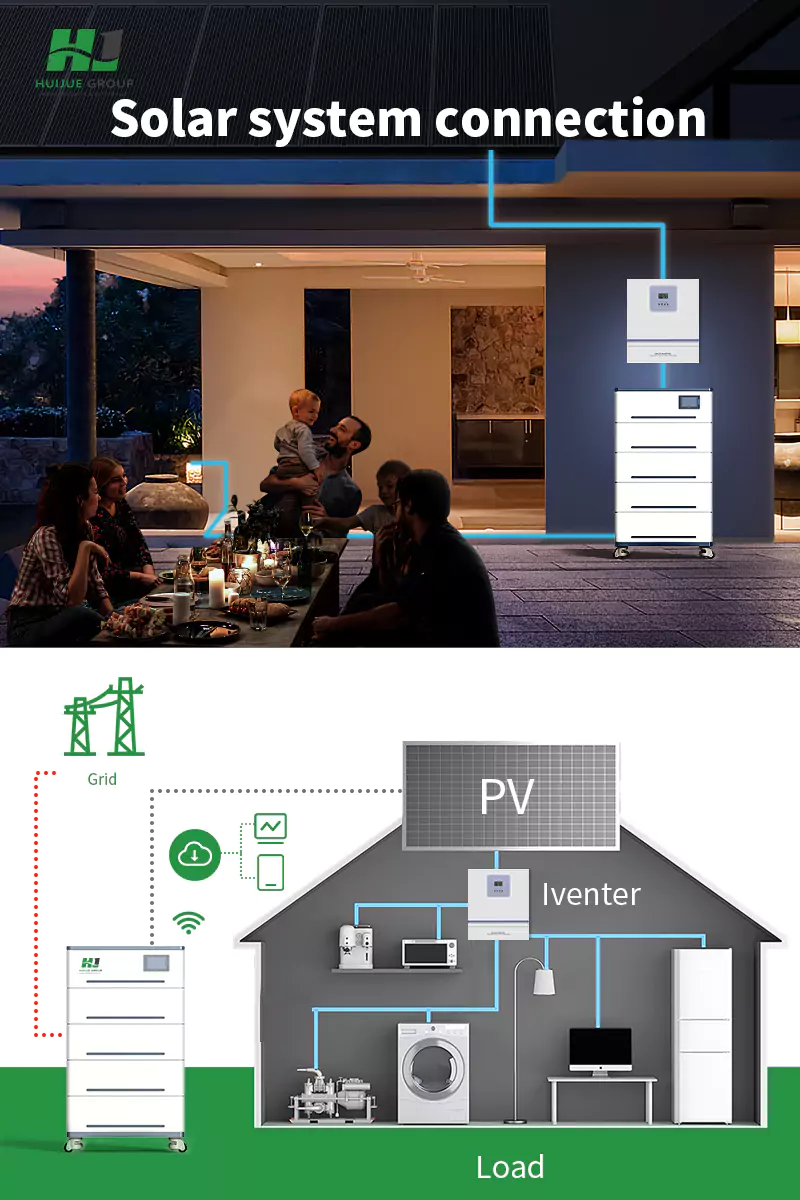
Table of Contents
- Understanding Home Solar Energy Systems
- Key Components
- Types of Systems
- Installation Process: Step-by-Step
- Pre-Installation Planning
- On-Site Execution
- Post-Installation Checks
- Application Types: Off-Grid vs. Grid-Tied
- Off-Grid Solar Systems
- Grid-Tied Solar Systems
- Pros and Cons of Home Solar Energy Systems
- Advantages
- Disadvantages
- Maximizing Your Solar Investment
- Tips for Efficient System Operation
- Incentives and Rebates
1. Understanding Home Solar Energy Systems
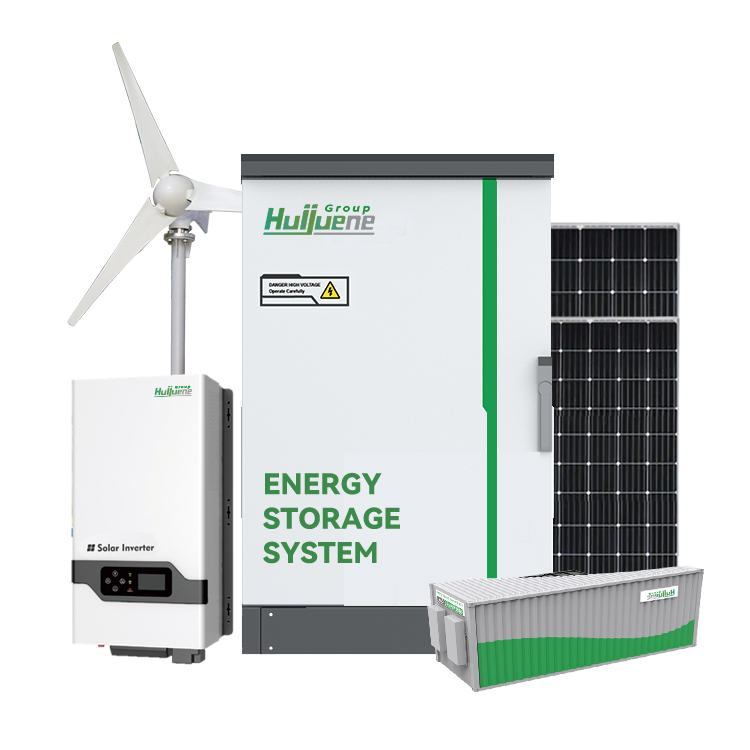
Key Components:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Photovoltaic Panels | Convert sunlight into direct current (DC) electricity |
| Batteries | Store excess energy generated by the panels for later use |
| Inverter | Convert DC electricity into alternating current (AC) for household appliances |
| Charge Controller | Regulates battery charging and discharging to prevent overcharge or deep discharge |
| Wiring & Connectors | Ensure efficient power transfer between components |
| Mounting System | Securely holds panels in place, optimizing sun exposure |
Types of Systems:
- Standalone (Off-Grid): Ideal for remote locations or areas with unreliable grid power. Entirely self-sufficient, requiring batteries for energy storage.
- Grid-Tied (On-Grid): Connected to the utility grid, allowing excess power generation to be sold back to the grid. In case of insufficient sunlight, the grid provides backup power.
2. Installation Process: Step-by-Step
- Pre-Installation Planning: Site assessment, design, and permit acquisition.
- On-Site Execution:
- Mounting system installation
- Photovoltaic panel placement and wiring
- Battery bank and inverter setup
- Electrical connections to the grid (for grid-tied systems)
- Post-Installation Checks: System testing, commissioning, and final inspections.
3. Application Types: Off-Grid vs. Grid-Tied
- Off-Grid: Perfect for cabins, farms, or areas with unreliable grid access. Offers total energy independence but requires careful management of energy usage and storage.
- Grid-Tied: More prevalent in urban and suburban areas. Enables net metering, where excess energy can be credited towards future electricity bills or sold to the utility company.
4. Pros and Cons of Home Solar Energy Systems
Advantages:
- Environmental Benefits: Reduces carbon footprint and promotes clean energy usage.
- Cost Savings: Long-term electricity bill reduction and potential income through net metering.
- Energy Independence: Decreases reliance on the grid, especially during outages.
Disadvantages:
- Initial Investment: High upfront costs for equipment and installation.
- Weather Dependency: Solar production is directly affected by sunlight availability.
- Maintenance Needs: Regular checks and cleaning are necessary to maintain optimal performance.
5. Maximizing Your Solar Investment
- Efficient System Design: Ensure panels are optimally oriented and tilted for maximum sun exposure.
- Regular Maintenance: Keep panels clean and monitor system performance for maximum energy output.
- Take Advantage of Incentives: Utilize government subsidies, tax credits, and rebates to offset installation costs.
Conclusion:
Home solar energy systems represent a promising future for clean, reliable, and cost-effective energy solutions. While they come with a significant initial investment, the long-term benefits in terms of cost savings, energy independence, and environmental impact make them a worthwhile investment. By understanding the components, installation process, application types, and weighing the pros and cons, households can make an informed decision about embracing solar power and unlocking the power of the sun.

















 Inquiry
Inquiry Online Chat
Online Chat