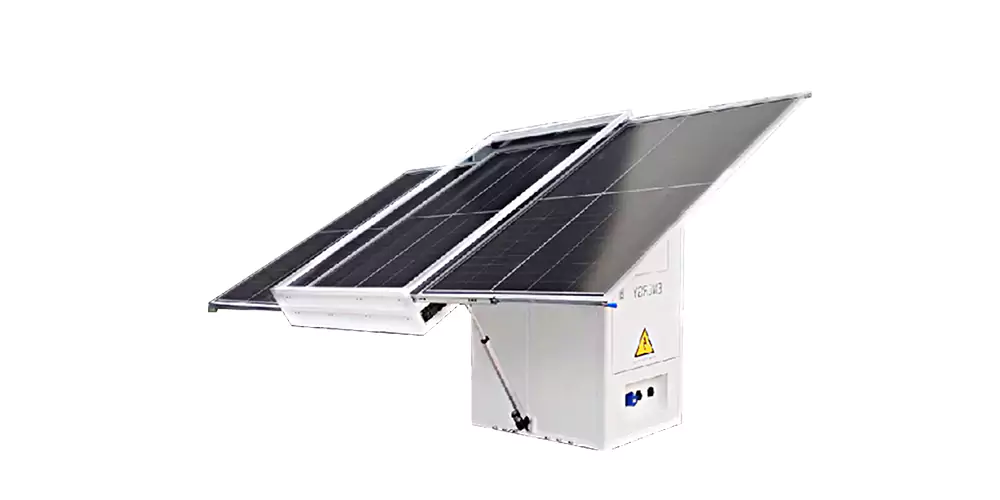
Besides that, thin-film photovoltaic panels, like CIGS or perovskite, are also light and flexible. Thin-film panels are made from non-silicon materials including but not limited to copper indium gallium selenide-CIGS and perovskite-which come with distinct advantages with regard to installation and application. The majority of the thin-film panels have low costs and thus find their perfect application area in Building Integrated Photovoltaics-BIPV and those specific applications that require lightweight or even flexible materials. The CIGS panel has a conversion efficiency of 7-13%, but perovskite uses an immense amount of theoretical efficiencies above 30%. Its commercial applications still form the early stage and require further development in order to achieve stability and durability. Organic photovoltaic panels are made of organic materials acting as their active layer. Organic panels are low-cost and ecologically friendly with quite good performance in poor light conditions. They are flexible and can adapt to some low-power electronic devices for certain niche applications, although their conversion efficiency and stability are relatively limited.
The general development trend of the photovoltaic industry is one of diversification, with different types of photovoltaic panels playing an important role in differing applications. Monocrystalline silicon panels can be used on large projects in pursuit of high efficiency, while polycrystalline panels can be used in small projects due to their relatively low cost. Thin-film panels are extremely suitable for BIPV applications, flexibility-requiring scenarios, while organic PV panels have good potential to realize their application in some specialized markets that require flexibility and low light efficiency. In the end, when going into great detail about the characteristics, application, and market positioning of each PV panel type, one can gauge that various PV technologies will be important in solving a number of energy requirements. Ongoing technological innovation will continue in the future, and increasing market demand will optimize and develop various types of PV panels to cater to different needs in the global transition toward clean, sustainable energy.

















 Inquiry
Inquiry Online Chat
Online Chat