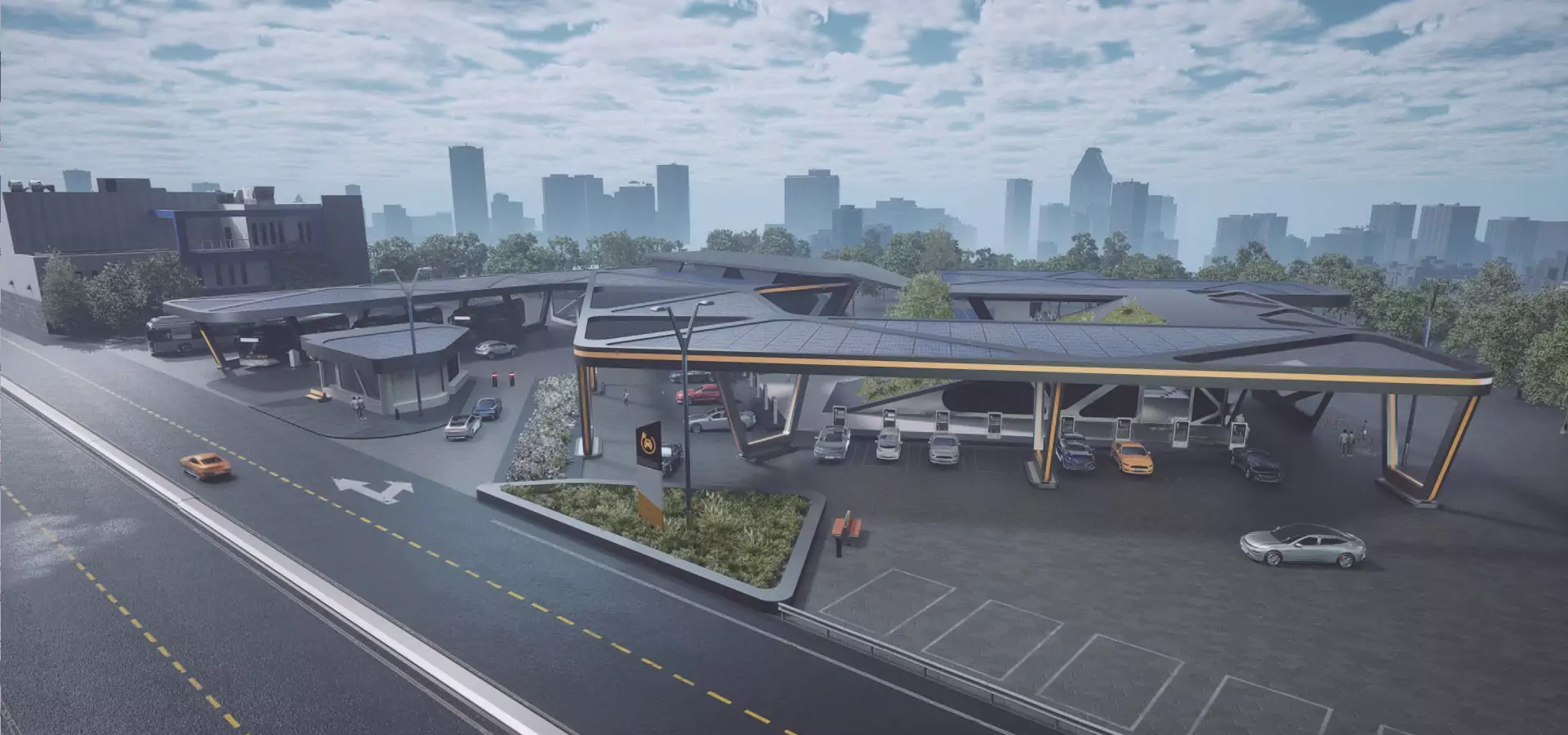

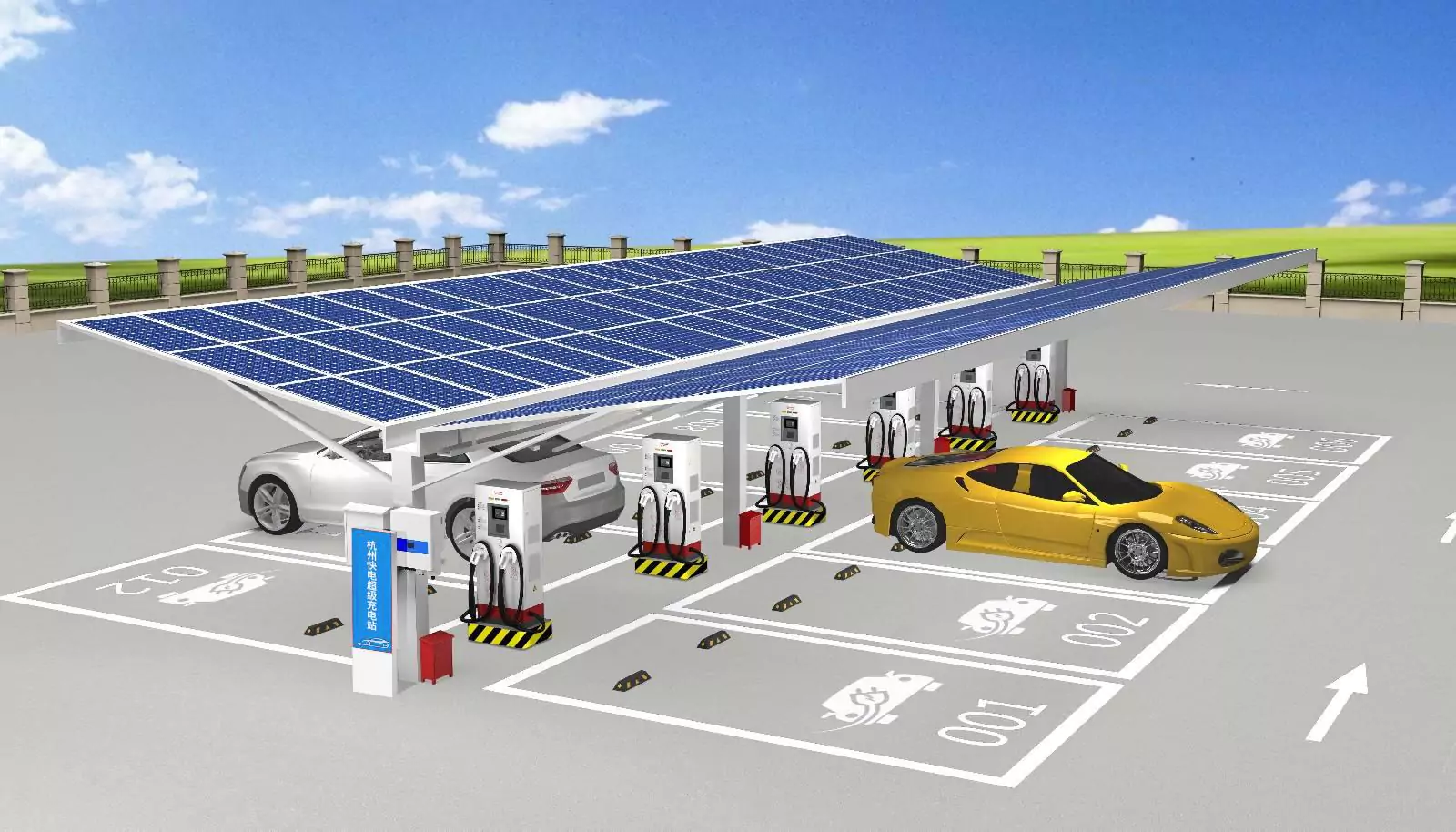
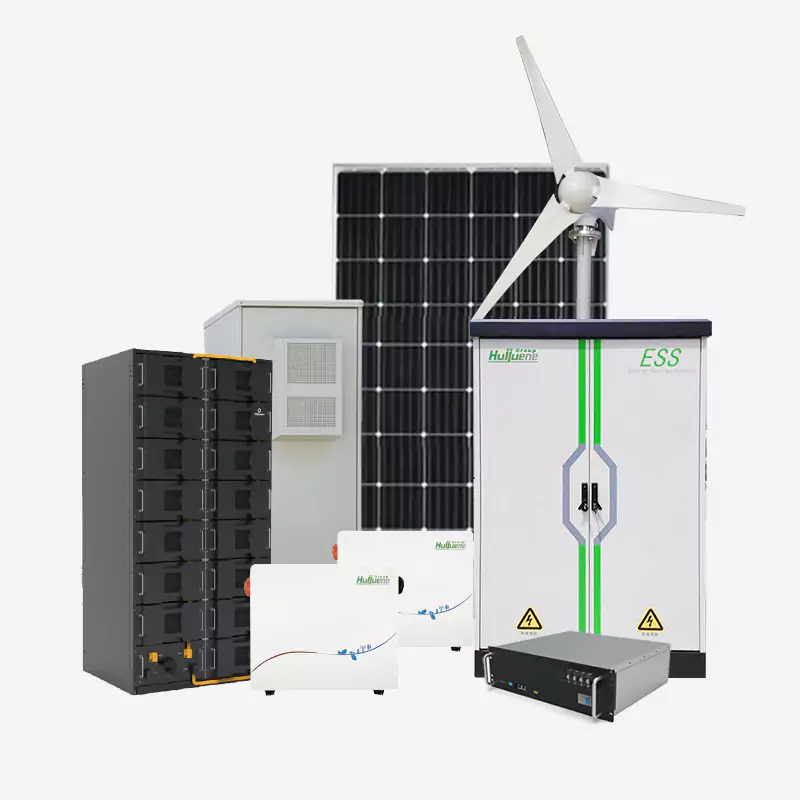
The integration of Smart Battery Energy Storage Systems (Smart BESS) into the EV charging stations is very important for developing advanced EV infrastructures. These systems advance the efficiency, flexibility, and user experience, which in turn help the growth of the EV market through intelligent energy management. Functionality, trends, and applications of Smart BESS in EV charging stations are discussed along with the best practices concerning station design.
I. INTRODUCTION TO INTELLIGENT BATTERY ENERGY STORAGE SYSTEMS
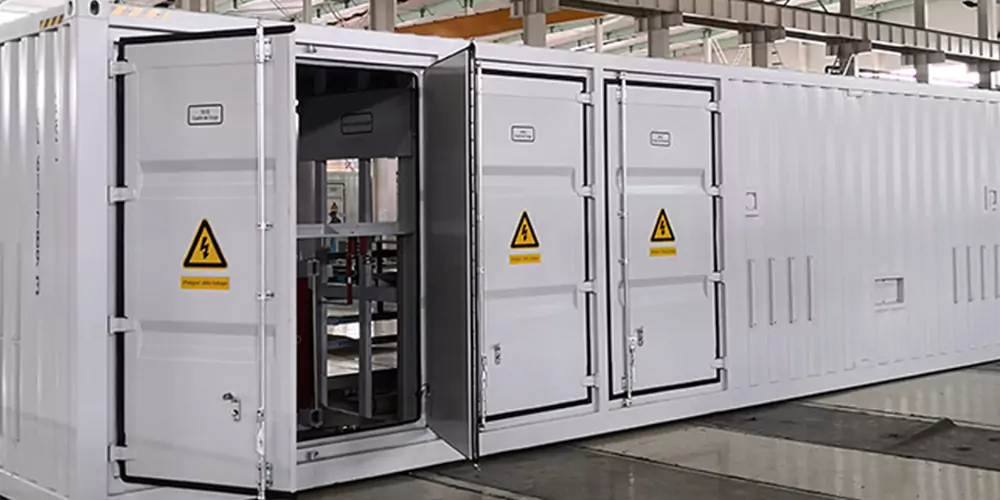
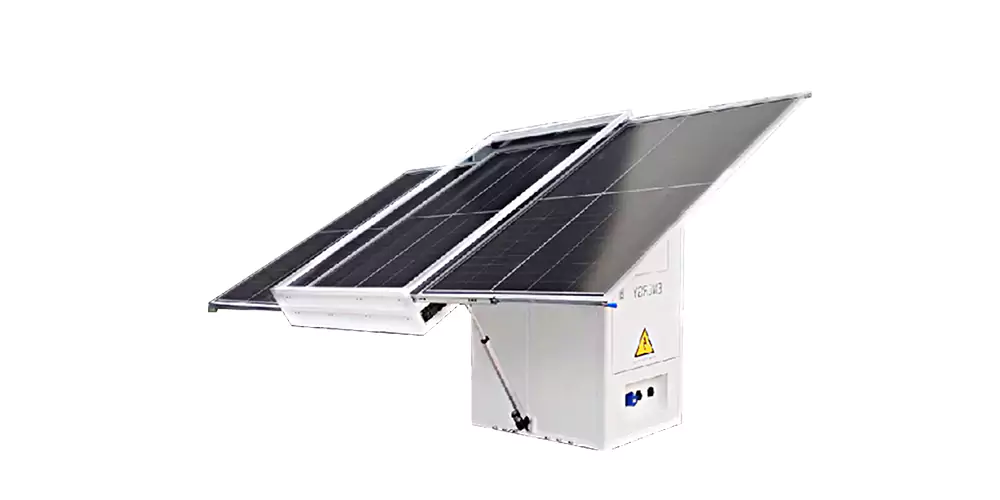
Smart BESS is a form of advanced system for efficiently storing and managing electrical energy. Equipped with sophisticated BMS, these systems monitor the state and performance of battery packs. Core components include the cells, charging modules, inverters, and data acquisition systems, which all contribute to enhancing storage and dispatch capabilities. In this sense, BMS software provides real-time capability insights and regulation toward making optimal decisions in terms of energy management regarding EV charging demand.II. Key Trends in Charging Technology
Since the EV industry is developing at a rapid pace, so does the charging technology, including trends such as the following:High-Power Charging: Long-term, high-power charging systems are moving toward megawatt-level charges since EVs are evolving. This will ensure faster and more efficient charging sessions than ever before.
Wireless Charging: Improvement in the circle of accessibility and safety, wireless charging ensures seamless, contact-free energy transfer to further enhance the user experience.
Battery Swapping: Though compatibility is still an issue, battery-swapping solutions are in development to provide fast refueling options for compatible models.
Integration of V2G: V2G will enable bidirectional energy flow between the EV and grid, facilitating the discharge of energy from the vehicle during peak demand periods and thus helping stabilize the grid.
AI-Optimized Dynamic Charging Systems: Such systems employ AI to dynamically optimize wireless charging processes, increasing their efficiency and safety.
III. Applications of Smart BESS in EV Charging Stations
Smart BESS has many other roles that add to the functionality and sustainability of the charging station for EVs:Energy Dispatching: Smart BESS works out load balancing in order to ensure stable grid integration by changing their charge/discharge rates and reducing demand surges during peak hours.
Data Collection and Analysis: The cloud-edge-based technology behind these systems captures huge data that energy storage enterprises use to develop better operation strategies.
Adaptability to Multi-Scenarios: Smart BESS meet diverse demands, especially from renewable energy-driven environmental needs, through grid-forming for reliable wide-area energy distribution across diverse scenarios.
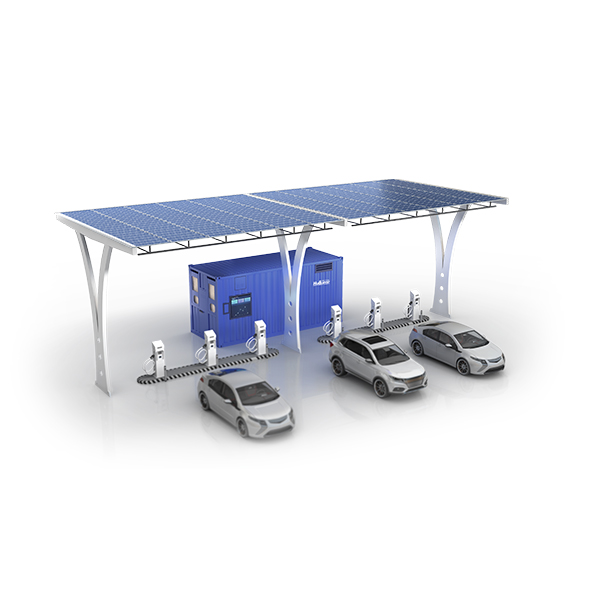
IV. Design and Construction of Intelligent EV Charging Stations
Efficient and user-friendly EV charging station design is essentially underpinned by strategic design and effective hardware-software integration:Hardware and Software Integration: The use of both hardware and software in smart charging stations can thus allow intuitive HMIs when operating them.
Facility Layout: Reasonable planning of the location of charging piles can reduce a series of problems such as limited access in residential areas, thus improving accessibility and user experience.
Operation Data Management: Users can monitor station status, charging, and revenue data remotely to enhance transparency and operation management.
Smart networking of BESS at EV charging stations is changing the paradigm of energy management towards a better experience for users while contributing to the sustainable energy goals. Since technological advancements are incessant, such intelligent stations will, indeed, be very key in the EV ecosystem by showing a way forward toward greener and more efficient transportation infrastructure.



















 Inquiry
Inquiry Online Chat
Online Chat