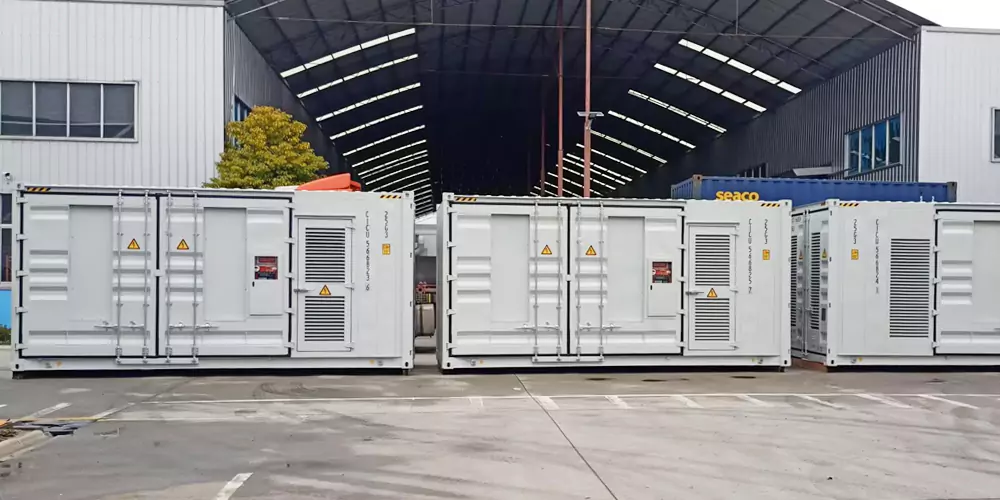
1. Understanding the Core Components of a BESS
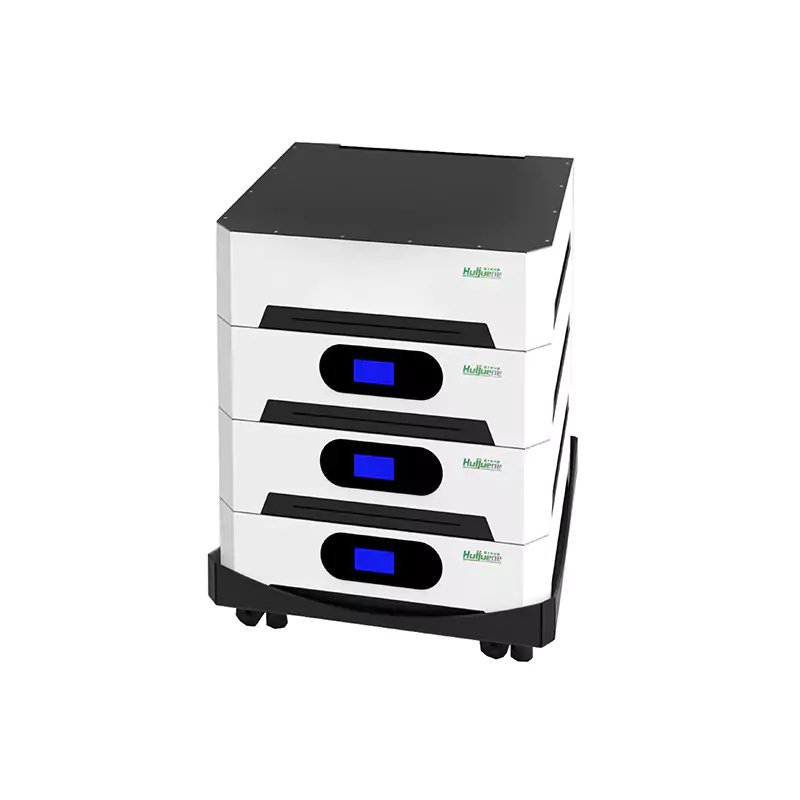
A general BESS assembly consists of a number of key components, integrated into one unit for effective energy storage, management, and distribution. These include:Battery Module: Battery modules represent the core of any BESS and are typically assembled from lithium-ion or lithium iron phosphate cells storing and releasing energy through electrochemical reactions. The BMS maintains the health of the batteries, controls charge/discharge cycles, and safeguards the cells against overcharging, overheating, and other possible risks.
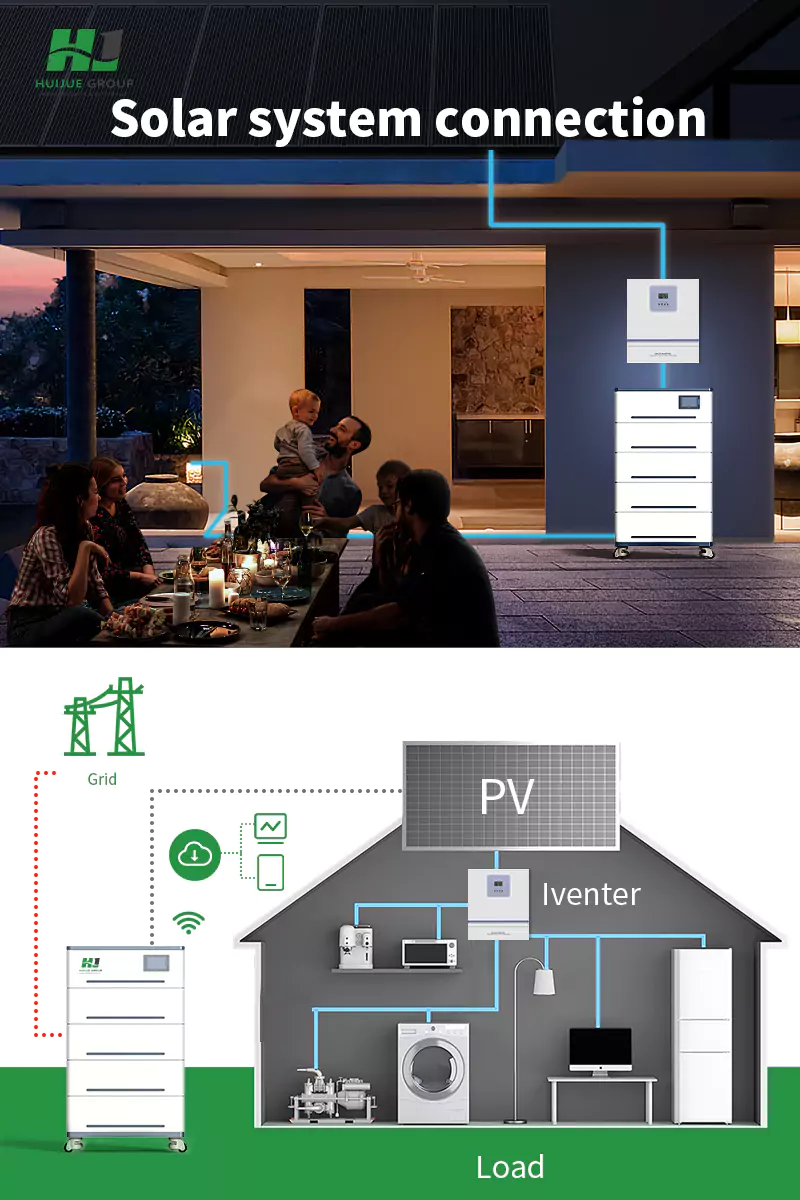
Inverters: The major role of the inverter is the conversion of DC stored in batteries into AC compatible with the grid and the end devices. Cooling Systems: Good cooling mechanisms are designed to maintain the optimal temperatures within the BESS to elongate the life of the batteries and avert thermal runaway. Control and Monitoring Systems: These perform real-time data acquisition, remote monitoring, and are designed for an interface with grid interconnectivity. It thereby ensures that the BESS responds to changes in demand at the grid end.
2. The Assembly Process: A Step-by-Step Overview
The assembly process is very critical in each and every step of BESS. The main steps in sequence are as follows:Component Preparation: Initial quality checks and preparation of various key components such as battery modules, BMS, inverters, etc. This stage ensures that every part meets its particular performance standard without defects.
Battery Module Assembly: Modules have to be put together into large battery racks, with very much emphasis on the calibration of voltage and capacity consistency of different cells.
Integration of BMS and Inverter: Each BMS is configured with respective battery modules; at the same time, placing inverters for the management of AC/DC conversion is conducted.
Installation of Safety and Control Systems: In this stage, the installment of circuit breakers, disconnect switches, and cooling systems is installed, then integrated with monitoring systems to provide the possibility for system oversight.
System Testing and Commissioning: Extensive testing is conducted to ensure that every component performs as it should under different load conditions. The tested BESS is then connected to the grid and commissioned into operation.
3. Key Considerations in Effective BESS Assembly
Following are a few considerations which become very important while assembling an effective and reliable BESS:Safety Protocols: Because BESS handle a high amount of energy, strict safety protocols will be paramount, including fire suppression systems, temperature monitoring, and emergency shutdown procedures.
Scalability: These systems are designed to be modular so that they could be expanded if energy needs increase. Ensuring each component can integrate smoothly with future upgrades is one of the big design considerations.
Efficiency and Sustainability: BESS efficiency is widely based on minimizing energy loss throughout the system. Other important facts that can help in attaining such an objective include material recycling and the use of environmentally friendly cooling solutions.
Compliance with Standards: The system shall conform to applicable standards, including but not limited to safety, reliability, and grid compatibility codes, such as UL, IEC, and NFPA, among others.

















 Inquiry
Inquiry Online Chat
Online Chat