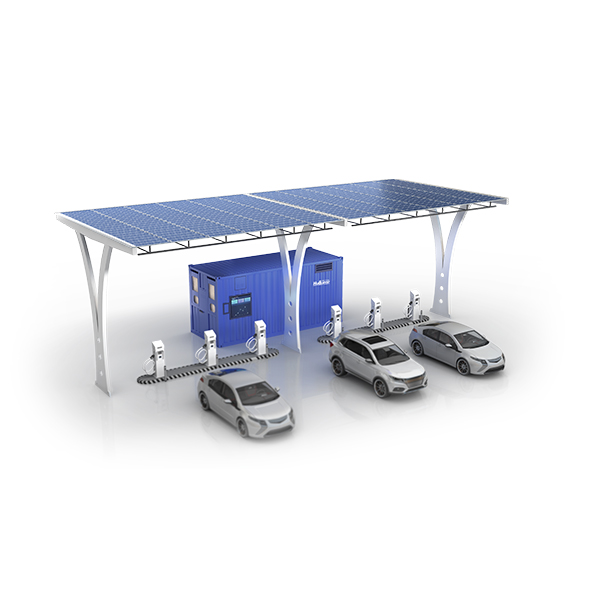
BESS plays an important role in modern energy management; hence, each has its advantages in different applications. LIBs are the most prevalent BESS, due to their superior energy density, high rate charge/discharge capability, and very long cycles, which make them superior in many advanced applications such as utility-scale storage, electric vehicles, and renewable energy systems. Present challenges with LIBs concern higher costs, thermal management requirements, and fire hazards.
Compared to these, lead-acid batteries are more affordable and reliable, have been in use for over a century, although they boast of lower energy density and a shorter life cycle. They find wide application in automotive, UPS systems, and backup power supplies, but their use requires regular maintenance.
Among these batteries, NaS batteries have some promising features such as high energy density and efficiency, which may turn them out to be very useful for applications of grid-scale storage. Operating at very high temperatures increases the system complexity and costs of NaS batteries. Safety-related electrolyte leakage further limits their applications.
Among all of the grid applications, flow batteries are known for their long-duration, discharge capability with scalability, featuring very high cycle life. Due to their modular nature, it is easy to scale up; however, they have lower energy density and higher system complexity, which results in higher upfront costs.
Overall, BESS technology selection involves considerations of various factors such as cost, performance, safety, and environmental impact. Lithium-ion technology will continue to be adopted for high-energy applications; however, a number of other options do exist, including lead-acid and flow batteries, which can become alternatives for cost-sensitive or long-duration requirements. BESS technology will continue to evolve as time goes on and will further support the integration of renewable energy and enhance resilience in the grid during this global turn toward sustainable power solutions.

| Battery Type | Energy Density | Cycle Life | Charging/Discharging Speed | Cost | Safety | Primary Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lithium-Ion | High | Long | Fast | High | Medium | Grid, EVs, Renewables |
| Lead-Acid | Low | Short | Slow | Low | High | Automotive, UPS, Backup |
| Sodium-Sulfur | High | Long | Moderate | Medium | Low | Grid, Industrial |
| Flow | Low | Very Long | Moderate | High | High | Grid, Renewables |


















 Inquiry
Inquiry Online Chat
Online Chat